“Customer Culture is the cornerstone of organizational and digital transformations in companies. Building a responsive customer journey is the key to the success of your interactions with your various contributors: customers, employees, partners…”
D.Popiolek-Ollé
Do you say Culture?
Customer Culture is the set of values and beliefs of a company, reflected by the attitudes and behaviors of employees in order to ensure sustainable customer satisfaction.
Each company has its own culture, stemming from its history, its heroes, its spirit, its values, its vision, its operation processes…. That’s what makes the cie unique.
The more this culture is rich, shareable, the more customers and employees feel engaged. DNA, it is a soul of the company. Culture is built on a daily basis. There is a king of aura where the vision, the updated measure of the ambitions, the strategic management, of the intentions, the employees behaviors, the reputation of the products, the adaptability of the company to be responsive are linked.
Understanding how the company works, its codes, its managerial models, its heritage makes it possible to analyze where it stands in the employee-employer relationship.
- Example: A paternalistic company can make the decision to transform into a liberal company, but the deployment of the new organizational structure will come up against the reflexes and ancestral processes that are well anchored in its way of producing and delegating power.
The first step of your design experience with your customers starts by understanding where the code, and the DNA of the company.
- Start by identifying the coat of arms of the cie
Modeling the user experience will require building your customer culture step by step, directing all of your actions in order to create a concrete and convincing experience with your customer, and thus create a simple journey for our users on the entire value chain that constitutes the company.
Building a customer culture by using UX design
UX Design (User eXperience Design) simply means the design of the user experience. To go further, UX encompasses all the emotions that users of a platform in question will feel. This platform can be a website or a mobile application for example.
Once the customer orientation has been adopted, UX design leads us to build a customer journey which is the result of the vision of our customers within our application tools.
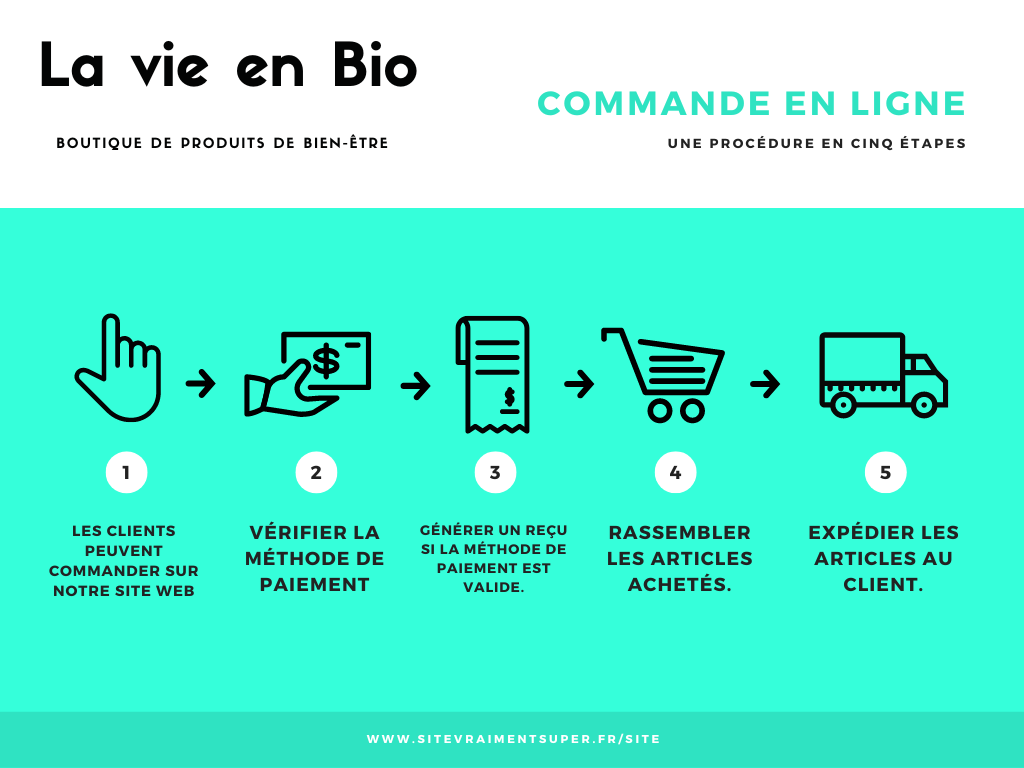
The objective of UX Design is to determine the functioning of the user interface in question and to make it as efficient as possible. This aims to limit the number of clicks required by the user to complete their journey. See the example on the right.
Why user design is important?
UX Design takes into account the WHY of user motivations. And the HOW/WHO of the methods used.
To optimize the user experience, you need to be user-centric first. You need to give your users what they are looking for in the best possible way. It is not to be focused on the graphic aspect, on the writing, on the animations, etc. The essential stages of optimization are:
The user experience aims to understand the needs of its users and create solutions based on the analyzes made on :
- An optimal conversion rate
- Better brand image
- Better SEO ranking in search engines
- More effective customer loyalty
- A better understanding of its users
Lead the user experience by limiting the number of click
UX, UX Design, UI : what are the difference between ?
How generate a good design for your user?
It’s putting yourself in your user’s shoes by identifying the main irritants.
Define your target and its path in 3 steps
The persona allows you to identify your key segment, and aligning your target with a understand of the persona’s needs.
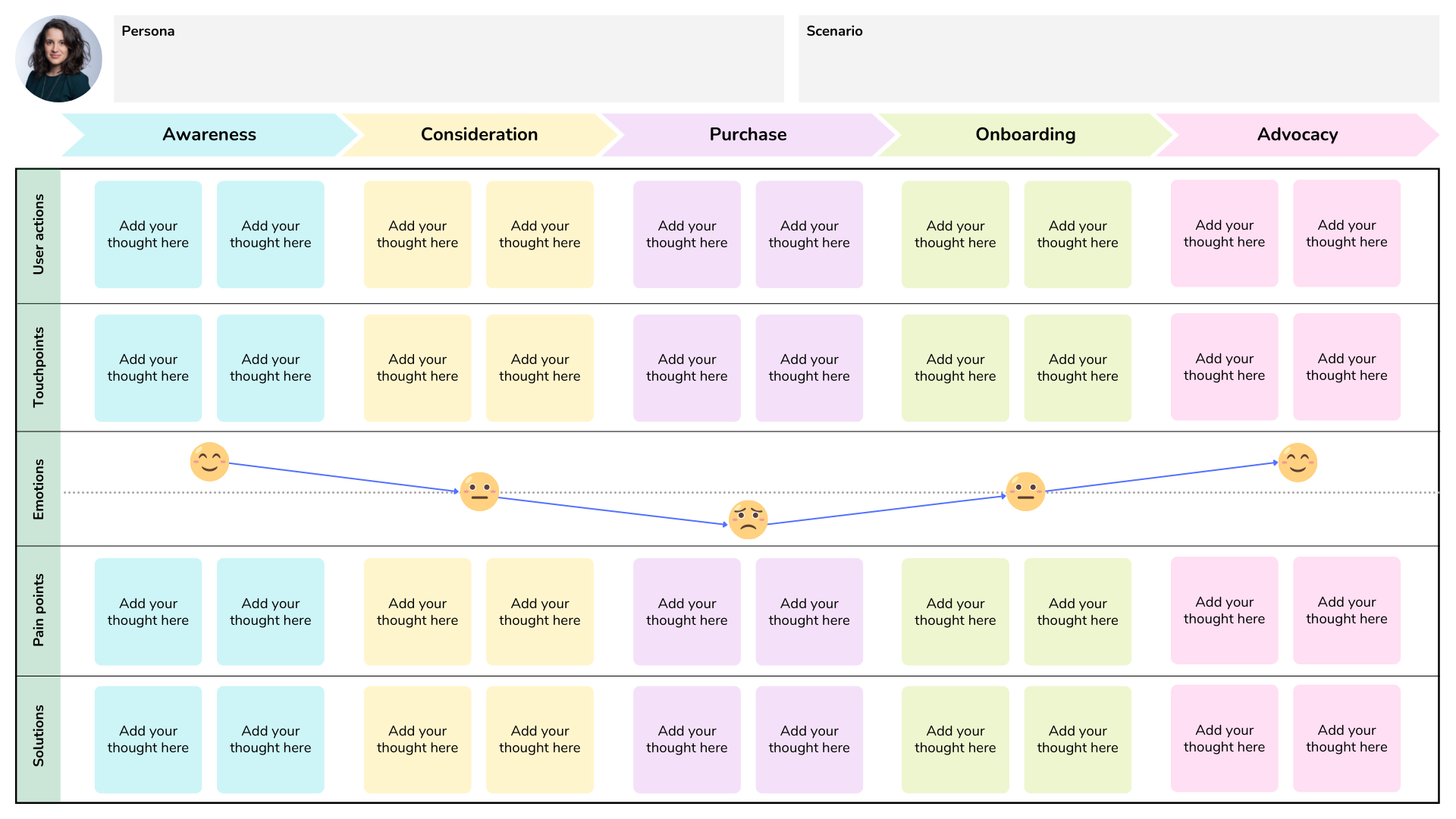
- Simplify the journey by removing irritants.
- Classify the irritants according to each step your user must take.
- Solved the issues and simplify the experience by reducing the number of steps
Many performance criteria are universal and don’t need a complex, in-depth study to be evaluated: loading time, browser/media compatibility, color consistency etc..
Tools to help you
- Heatmap: A heatmap will allow you to record the screen of your users and see where they navigate and where they pass their mouse precisely on your interface.
- A/B testing: A/B testing is a technique for testing two variations of pages to see which one converts better. Thus, by testing different structures, different texts, or functionalities, you will be able to compare the devices with each other.
- Surveys: You also have the option of somehow interviewing your users to ask them questions about your product and your interface. This way, you will see what blockages and frictions your users encounter and act accordingly.
- User testing: One of the most effective methods, user testing, allows you to directly see how users behave when faced with a given scenario concerning your interface.


 Once the customer orientation has been adopted, UX design leads us to build a customer journey that is the result of our customers’ vision within our application tools. The way …
Once the customer orientation has been adopted, UX design leads us to build a customer journey that is the result of our customers’ vision within our application tools. The way …